What is Diffusion coating?
Diffusion coatings, specifically aluminide diffusion coatings, are extensively used in various industries to enhance the performance and durability of metal components
These coatings involve the diffusion of aluminum into the surface of a metal substrate, resulting in the formation of a protective layer. Overall, these coatings play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of various industrial applications.
Flame Spray offers different kinds of diffusion coatings:
- Pt-Aluminides
- Si-modified Aluminides
- Standard aluminides
Platinum aluminide (PtAl) coatings are highly efficient to protect engine components against oxidation and the effects of combustion temperatures up to approx. 1,100°C. Si-modified aluminides are affordable and effective alternatives for the protection of turbines, fuel cells, boilers components up to approx. 900°C
Standard aluminides are widely used thanks to their flexibility. They are commonly used to protect the internal cooling passages and external surfaces of airfoils of Gas Turbines components, burners, fuel cells, nuts, bolts , etc. up to approx. 950°C.
Flame Spray proprietary technologies are applied on components of different geometry, dimensions and materials.
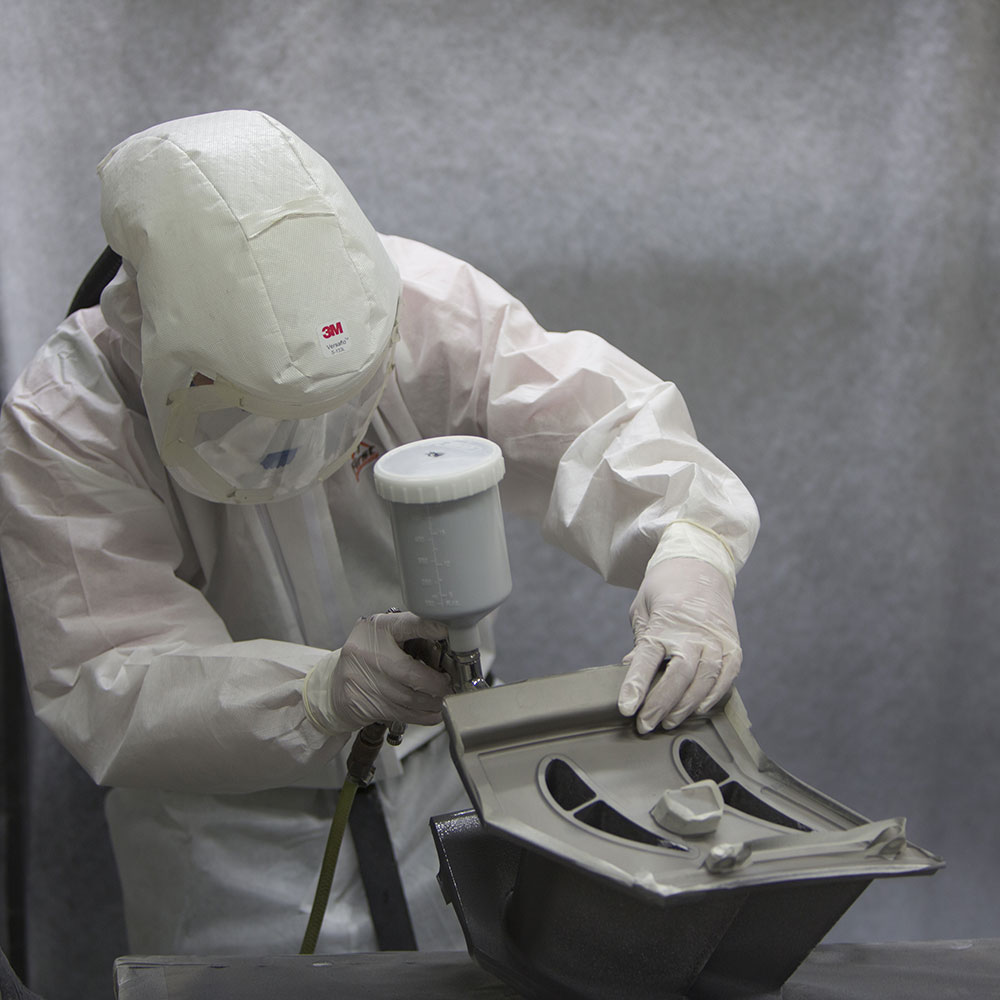



Advantages of Diffusion coating
One of the primary advantages of aluminide diffusion coatings is their ability to significantly increase the lifespan and performance of critical components in high-temperature environments.
The protective layer formed by the coating reduces the degradation caused by oxidation and corrosion, ultimately extending the service life of the coated parts. Additionally, aluminide diffusion coatings can improve the overall efficiency and reliability of gas turbine engines by reducing fuel consumption and minimizing maintenance requirements.
Results
Bring us your problems, our experience will provide the answers
We support and advise you in selecting the most suitable technology and materials to meet your specific needs.
Contact us now to have an engineer at your disposal, and together, we’ll find the solution to your biggest problems. We understand urgent, an engineer can be immediately available, call us, email us, and if necessary, you’ll have a proposal within 24 hours.
Diffusion coatings F.A.Q.
Diffusion coating is a process in which metal components that will be subjected to high temperature conditions and highly corrosive environments are coated with a non-corrosive material. The process is normally done at elevated temperatures in a controlled chamber.
The most widely used coatings are chromium, aluminum or silicon material. Substrate materials usually coated include cobalt and nickel-based super alloys, steels (including carbon, alloy and stainless steels) and refractory metals, among other alloys. As a result, the base metal develops extreme resistance to corrosion, oxidation and erosion in its severe working conditions. This makes the process highly reliable, enhancing the manufacture of critical components. Diffusion coating is normally used to process gas turbine engine components (vanes, blades and cases), pump impellers, gate valves and power generation components.
Coating thickness depends heavily upon the base material and allowed diffusion temperatures, but are usually in the range of 30-100 microns (0,001” – 0,004”)
